- Fire Sprinkler Head
A sprinkler head is a type of valve that is part of an automatic fire sprinkler system. It acts as a control mechanism for the release of water or other extinguishing agents when a fire is detected.
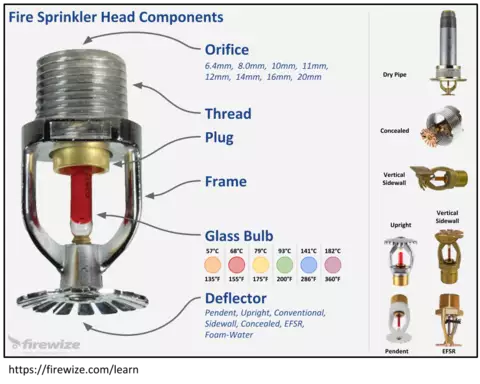
It consists of a frame, deflector, fusible element or bulb, orifice, and possibly a water seal. When a fire reaches a certain temperature, the fusible element or bulb breaks, allowing pressurized water to flow through the sprinkler head. The deflector directs the water in a specific spray pattern to control or extinguish the fire by absorbing heat and suppressing flames. Sprinkler heads are designed for various applications, with different activation temperatures, flow rates, and spray patterns to suit specific fire protection needs.
An automatic fire sprinkler system head, also known as a sprinkler head, is a key component of fire protection systems. It is a device designed to detect and control the spread of fires by releasing water or other extinguishing agents. The sprinkler head is typically mounted on the ceiling or walls and is connected to a network of pipes filled with pressurized water.
The construction of a sprinkler head can vary depending on the specific type and model, but most commonly, it consists of the following components:
- Frame: The frame is the outer casing of the sprinkler head, typically made of brass, bronze, or other corrosion-resistant materials. It provides structural support and houses the internal components.
- Deflector: The deflector is a metal plate or assembly positioned below the frame. Its purpose is to control the distribution of water from the sprinkler head. When a fire activates the sprinkler, the deflector directs the water in a specific pattern, typically in a circular or semicircular spray.
- Fusible Element or Bulb: This is a crucial part of the sprinkler head that holds back the flow of water. It consists of a small glass bulb or a heat-sensitive metal link. When exposed to a certain temperature, such as the heat generated by a fire, the element or bulb will rupture, allowing water to flow through the sprinkler head.
- Orifice: The orifice is a small opening located at the center of the deflector. It controls the flow rate of water released from the sprinkler head. The size of the orifice is carefully calculated to ensure the correct amount of water is discharged to control the fire effectively.
- Water Seal: In some sprinkler heads, there is a water seal at the base of the frame. The seal prevents water from leaking out of the sprinkler head until the fusible element or bulb is activated.
When a fire occurs, the heat generated raises the ambient temperature, causing the fusible element or bulb to break. This releases the pressurized water in the pipes, which then flows through the orifice and is directed by the deflector in a spray pattern. The water extinguishes or controls the fire by absorbing heat, cooling the surrounding area, and suppressing flames.
It's important to note that there are various types of sprinkler heads available, each designed for specific applications, such as residential, commercial, or industrial settings. They may differ in terms of activation temperature, flow rate, and spray pattern to suit different fire protection requirements.