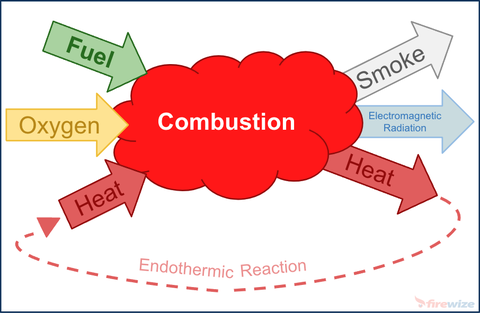
- Fire
Fire also known as combustion is a sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the by-products of combustion being; heat, smoke & electromagnetic radiation (light).
Four things must be present at the same time in order to produce combustion:
- Fuel —Any combustible material - solid, liquid or gas. Most solids and liquids must vaporize before they will burn.
- Oxidant — An oxidant (usually oxygen) - Sufficient oxygen must be present in the atmosphere surrounding the fuel for combustion.
- Heat — Sufficient heat energy must be applied to raise the fuel to it's ignition temperature
- Chemical, exothermic reaction — This reaction can occur when all three of the above elements are present in the proper conditions and proportions. Fire (rapid oxidisation) is the result of this chemical reaction.